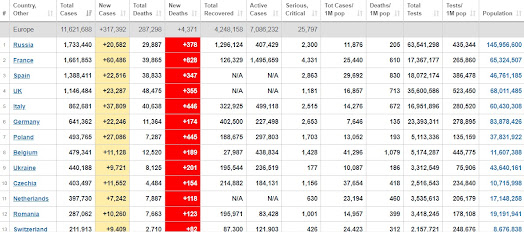
The world is reeling under another Corona wave, every day we are seeing more than six lakh new cases, and daily Corona death is touching 9,000. The situation is worsening day by day. Most of the European nations are going back to lockdown again. France, Germany, UK and Belgium have already started the move and others are likely to follow in the coming months.
Unfortunately, the world has not learnt little from the 10-month pandemic. We have forgotten it but CORONA is here to stay long. Ostrich like the attitude of state governments is not going to help anyone. High time to make SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) if we really want to fight the pandemic.
France is among the worst affected countries in Europe
cases have reached more than 16 lakhs, which is not great but its active cases are as high as 14.65 lakhs, which means only 1.26 lakh people have recovered so far.
But if we talk of new cases, more than 50 % of new cases are coming from Europe, of the new 6.27 lakh new cases on November 6, 3.15 lakh is from Europe alone. Death wise also out of nearly 9,000 daily deaths, around 4,800 is reported from Europe alone. And it shows the alarming spread in Europe.
After Europe, the USA is worst affected
We have been blaming Donald Trump for mishandling the situation. The fact is people of the USA are to be blamed for being complacent of the virus. They must remember they are not any terror group, but an invisible enemy about whom we know little despite our 10-month long research work.
Today, On November 6, it added 1.32 lakh new cases reported 1,248 new deaths. Total active cases are around 34 lakhs of the total 64 lakh cases reported so far.
USA is bussy in elections and forgets COVID-19, But CORONA has not forgotten the USA and working overnight spreading it all over the states. Let's see how new USA President deals with the pandemic.
India should learn from the bad experience of Europe, Kerala and Delhi
CPVID-19 spread in India and its recovery is much much better than Europe and USA. As against the population of 137 crores, India reported only 84 lakh cases out of which more than 78 lakhs have already recovered.
There are only 5.16 lakh active cases. With this India probably has the highest recovery rate and lowest fatality rate in the world.
Having said this, the fact remains Indian cannot sit on good performance like Germany and Hongkong and later face the wrath of complacency.
It is high time to be vigilant, and remember we can forget Corona but it would not forget us. Corona is no 20-20 match, it is here to stay long and state governments must learn to live with it
What we have learnt from 10-month long lockdown
https://statesmanvijay.blogspot.com/2020/07/10-simple-ways-to-prevent-viral.html
China had imposed its
first lockdown in Wuhan and other cities of Hubei on January 23 in wake of
COVID-19. It shocked the world initially, but later almost all countries in the
world adopted the same practice to contain the virus spread. Some did it
efficiently and some partially and some did lockdown for the sake of it.
Today it has been almost
10 months of starting the lockdown, the entire world economy is in shambles,
poor countries which are already cash-starved are hit the most. It did not
spare the world’s leading economies including USA, Germany, France and UK.
The decision to lockdown
was taken in haste as most of the governments were confused on how to fight
with this invisible enemy gifted by China. That time the step to lock down the
country was obvious and required.
It is sorry to say that
despite 10-month long research on the virus, most countries are still somewhat confused and going for the
old practice of shutting down the country. Little they realize that the
lockdown is no permanent solution. Poor people would die in any case either
because of COVID-19 or due to hunger.
It is time for
governments to evaluate whether to allow poor people to die of hunger or find a
better workable solution. Remember third world countries would follow Developed
countries footsteps. The world has apparently learnt little from COVID-19 and
hardly tried to find a solution to contain the virus.
Remember COVID-19 is just
a beginning, in the coming time we will see more contagious and stronger virus
than this. It is time to make an SOP (Standard Operating Procedures) to change
our lifestyle. Japan, Korea and China is the best example, they changed their
lifestyle to fight SARS and other such viruses.
I strongly recommend here
old Indian style of living, where People used to practice certain rules to
avoid such viral/bacterial diseases. (1) Like never cook without clean cloths
and without taking bath, (2) Not let anyone enter your kitchen (3) Not touch
anything after you return to form from the market, wash your face hand, change clothes
and then only interact with your family especially children (4) Do gargle
after every meal and always eat freshly cooked food.
Is Smart LOCKDOWN a Solution ?
To me smart lockdown and proper
COVID-19 Education may be a way out to contain the virus.
1)
Let economy work for
first five days a week.
2)
Tell people to
effectively maintain social distancing and use of mask at public places.
3)
Tell people not to visit
relatives until or unless it is very important.
4)
Do not let children playout for more than an hour that too strictly wearing masks.
5)
Strictly ask people to
have Hot Water (better a light Kada) every four hours. It helps build immunity
and fight the seasonal virus. (I have been doing this for 20 years to fight
seasonal virus stronger than COVID-19 and it worked perfectly).
6)
Ask people to change
their habits of taking your hands to mouth, eyes and noses.
7)
Tell people going out in
public places to wash their hands every two hours.
8)
Change your clothes
every time you return home from a public place.
9)
Avoid window shopping
and go where it is essential.
10) Prefer online shopping, whenever and wherever it is
possible.
ENDS.